Hypofractionated Radiation for Breast Cancer
4 min read
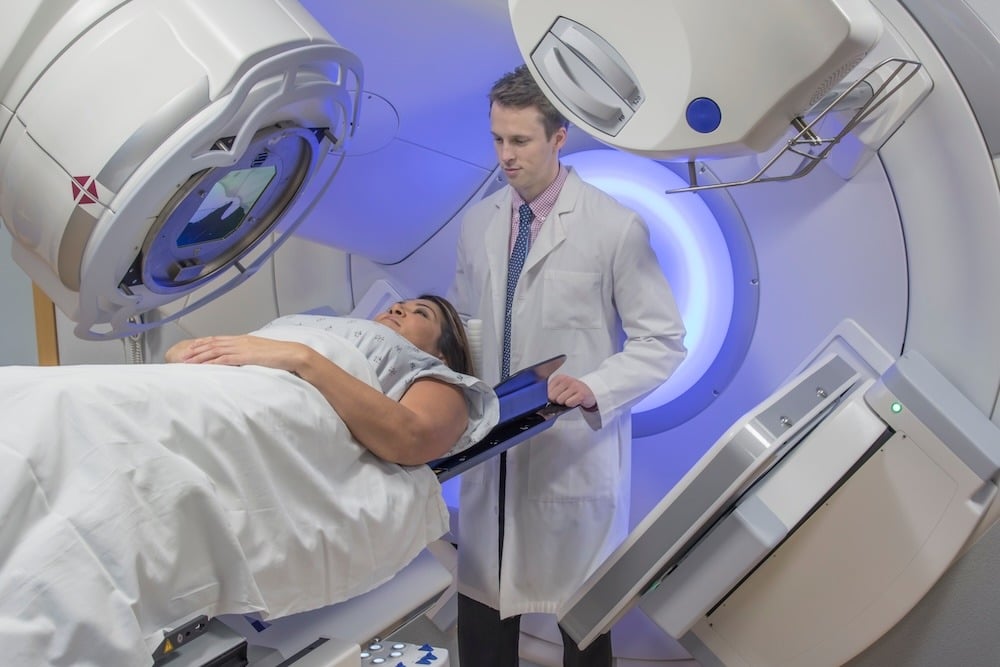
Radiation therapy is commonly used to treat breast cancer, usually in conjunction with other forms of treatment, known as a concurrent treatment. Traditional radiation therapy schedules require patients to receive the treatment five days per week for up to seven weeks. In recent years a slightly different approach, called hypofractionated radiation, has proven to cut down on the length of the treatment and can even lessen side effects.
Hypofractionated breast cancer radiation therapy may not be available to every patient. Your cancer care team will decide if it's suitable for you. This is because the expected results vary based on your unique factors. Every breast cancer journey is different, which is why it can be helpful to understand various treatment methods including radiation therapy options.
How Does Radiation Treat Breast Cancer?
Radiation therapy uses high-energy X-rays, or particles, to damage and kill cancer cells. For breast cancer, your oncologist may recommend radiation therapy after breast-conserving surgery to reduce the likelihood that the cancer will come back in the same breast or nearby lymph nodes. It's sometimes used after a mastectomy if the cancer covered a large area or involved multiple lymph nodes. And in some cases it's given before surgery is performed to shrink the size of the tumor.
The most common type of radiation used for breast cancer is called external beam radiation therapy (EBRT). A machine called a linear accelerator focuses radiation beams on the affected area from outside the body. These beams are specifically shaped to the area that's being treated. If the tumor is still present, the beams will conform to the shape of the tumor, reducing damage to nearby healthy skin.
If you had surgery to conserve the breast, you will likely have radiation that is focused on the entire breast.
How is Hypofractionated Radiation Therapy Different?
Typically breast radiation is given each day, Monday through Friday, for six to seven weeks. Hypofractionated radiation can reduce the number of weeks treatment is needed.
The patient receives the same overall dose of radiation but in a shorter period of time, often in three to four weeks. This means the patient is getting a higher dose at each session. Studies have shown that for women who had breast-conserving surgery and whose cancer has not spread to the lymph nodes, hypofractionated radiation is just as effective at preventing cancer from returning in the same breast as traditional external beam radiation therapy.
Benefits of Hypofractionated Radiation
Hypofractionated radiation has several benefits.
Shorter radiation therapy schedule - This is the most obvious benefit, making it easier for most people to manage.
Lessened side effects - Typical side effects of radiation for breast cancer patients include:
- Blistered skin
- Pain in the radiation site
- Skin irritation and burning or stinging skin
- Fatigue
Studies have shown that the percentage of patients who experience these symptoms is significantly less after hypofractionated radiation than after standard radiation. Recently, a new study found that an even shorter schedule of accelerated radiation provides the same benefits to patients who have early-stage breast cancer.
Same reduced risk of recurrence compared to standard radiation therapy. According to the study, patients with early-stage breast cancer who received five treatments in one week, totaling less than the dosage of a three-week schedule, had the same reduced risk of recurrence as the people who received radiation treatment over a three-week period. Amazingly, the side effects were similar in both groups. The study took place over a period of five years.
It's much easier for patients to complete all of their treatments. Six to seven weeks is a long time to commit to treatments 5-days a week. With a shorter commitment patients were more likely to complete all their treatment and this means more positive outcomes.
At Rocky Mountain Breast Specialists, we are relentlessly driven to providing you with the best treatment experience possible.
Whether before, during, or after treatment, our whole breast cancer team is dedicated to ensuring you are equipped with the tools and knowledge for success. Our experts may recommend different treatment methods, based on your unique circumstances.
Cancer Care You Can Count on at Rocky Mountain Breast Specialists
At Rocky Mountain Breast Specialists, our compassionate providers are dedicated to giving you the highest quality care while making your breast cancer treatments as stress-free as possible. Using a team-based approach, we develop a personalized treatment plan based on your unique diagnosis and other personal factors. Our multidisciplinary team works together to ensure treatment starts as quickly as possible, leading to the best possible outcomes.
Whether you or a loved one develops breast cancer, or any other type of cancer, we can help you through the treatment journey. With locations across Colorado, we treat more cancer patients than anywhere else in the state. As a member of The US Oncology Network, we have access to more clinical trials than any other facility in the state. We pride ourselves on providing the most optimal cancer care in the region.
Throughout the treatment process, we are with our patients each step of the way. From offering financial counseling services to joining support groups, patients have all of our resources supporting their optimal treatment process. That support is not just limited to our patients. We have support groups that are open to caregivers as well.

